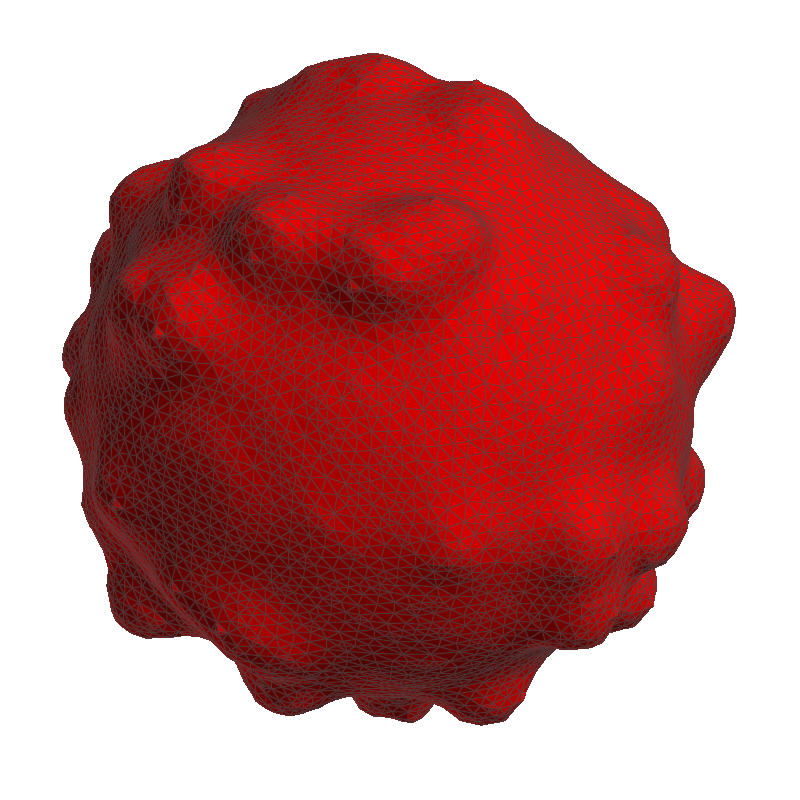
Smooth Mesh
Meshes from voxel structures often have a significant surface roughness which can be reduced by applying smoothing filters. In MeshGeo, three smoothing filters are selectable from the pull-down menu to improve the mesh quality: Taubin, Laplacian, or Constraint Laplacian. Choose a filter and click Smooth to apply the selected filter to the current mesh.

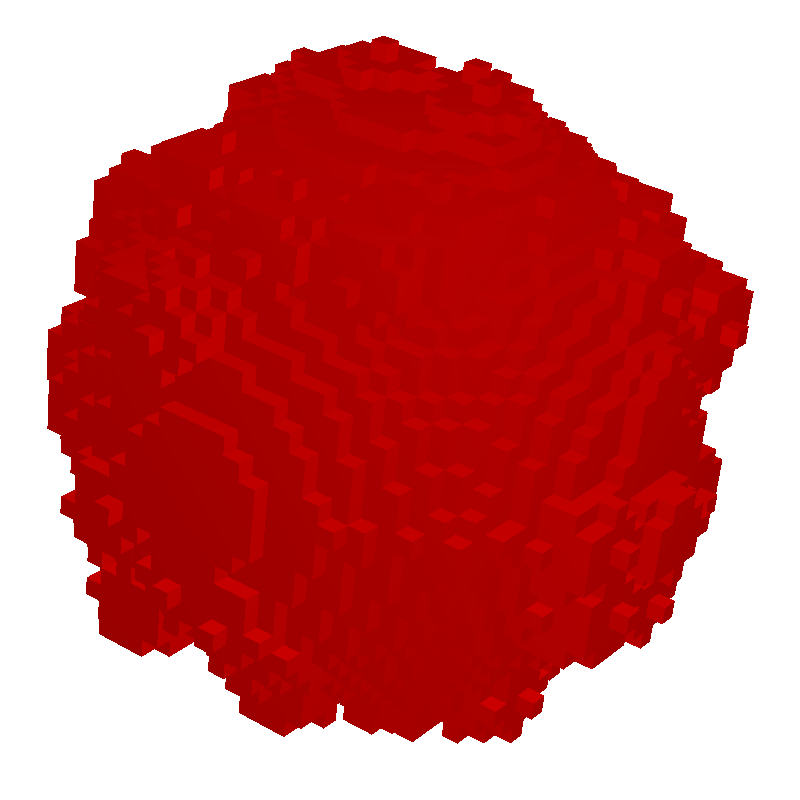
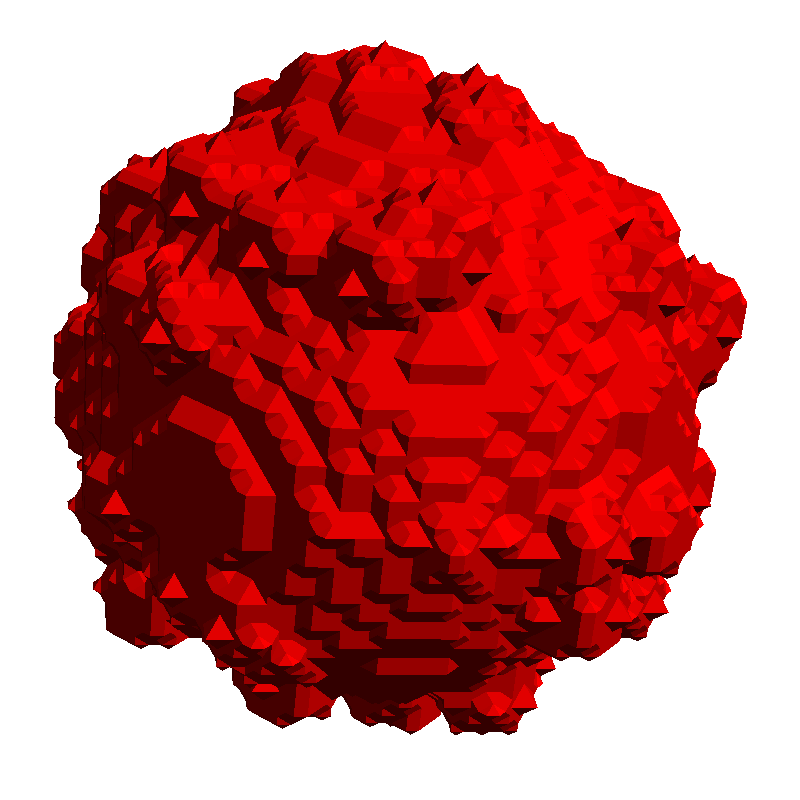
Smoothing is best shown on a structure with an irregular surface. The example structure created here is a grain with surface roughness. The original mesh before smoothing is created with Create Mesh → Create Voxel Mesh and the Multi Material mode.
To observe the differences between the mesh types, it is recommended to set the View Mode to Faces and Wireframe (Triangles tab → View → Faces and Wireframe, in the Visualization panel above the Visualization area).
Voxel structure
|
  |
  |
|
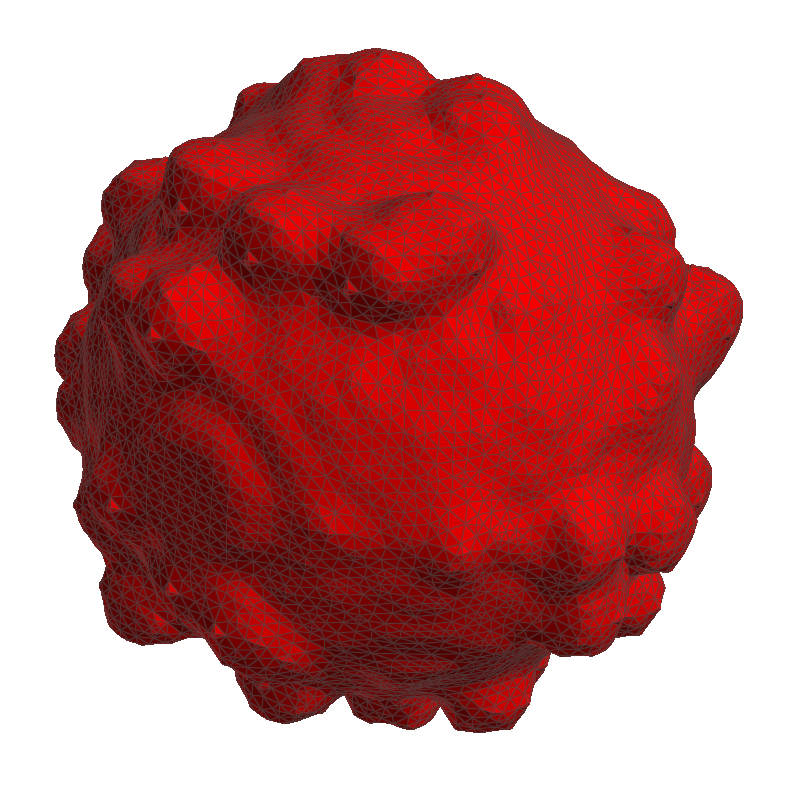
The Taubin filter iteratively combines different Laplacian filters to provide better volume preservation. The runtime for Taubin is longer than for Laplacian. In the screenshot on the right, observe that the mesh is rougher than the result after Laplacian filtering, while its volume is closer to the volume of the original voxel structure. Find more information on the Taubin filter in the References. |
Taubin filter |
||
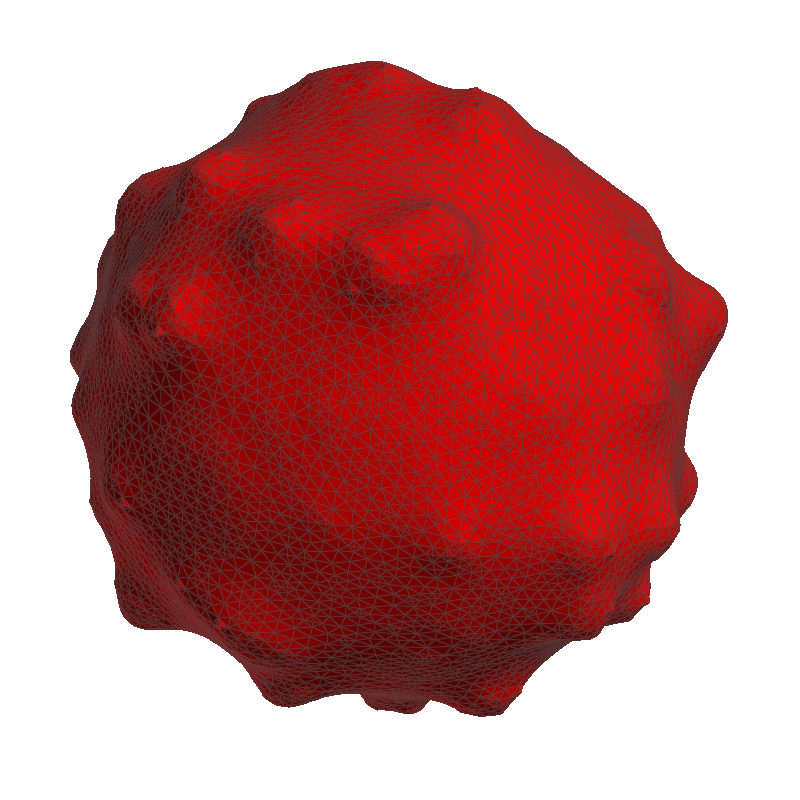
The Laplacian filter is a simple and fast option for mesh smoothing. However, this filter causes mesh shrinking for most geometries. For further information, see Wikipedia: Laplacian Smoothing. |
Laplacian filter |
||
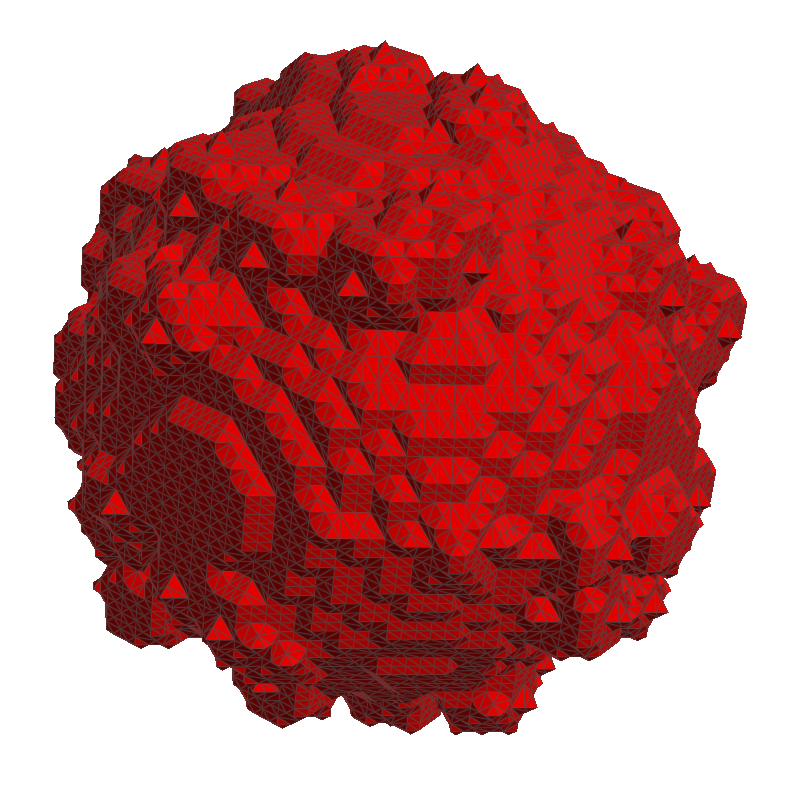
The Constraint Laplacian filter is a derivation of the Laplacian approach, but it ensures that points from the triangulation stay in the voxel they originated from. This results in an even better preservation of the volume, but it can also lead to artefacts in the mesh. |
Constraint Laplacian filter |
||